Production and uses
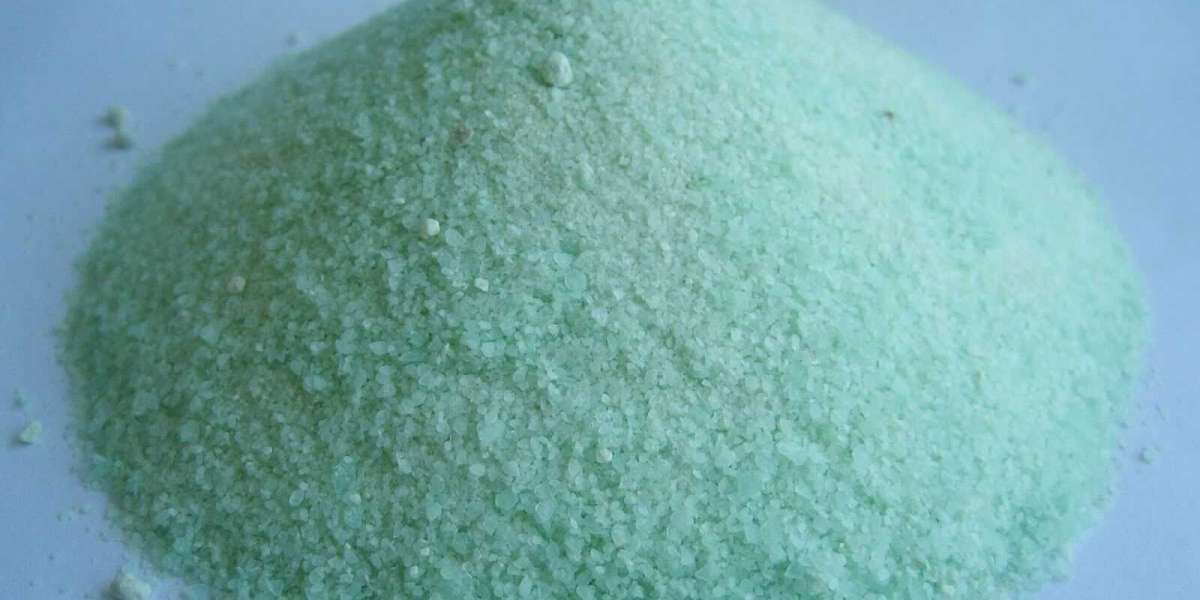
Ferrous sulfate is widely used in various industries and is one of the important ferrous metal chemicals produced globally. It is manufactured by reacting ferrous metal like iron with sulfuric acid in an exothermic reaction. The annual worldwide production capacity of ferrous sulfate stands at over 5 million tons currently. The major producers of this chemical are China, India, Russia, and several European nations. It finds applications in sectors like water treatment, agriculture, paints coatings, pharmaceuticals, construction, etc. due to its properties.
Water treatment industry is one of the largest end-users of Ferrous Sulfate. It is dosed to water as a coagulant to remove suspended solid particles and other impurities during purification processes. This helps in clarifying and disinfecting water. It also aids in controlling algal blooms and aquatic plant growth in lakes and reservoirs. The agricultural sector utilizes it as a fertilizer supplement for crops to provide Iron which is an essential micronutrient. It is also used as an additive in animal feed to prevent Iron deficiency in livestock.
Role in paints and coatings manufacturing
Iron (II) sulfate finds an important application as a paint pigment and mordant in paint and coatings manufacturing. It acts as a primary pigment in specialty paints meant for metal substrates, giving a distinctive blue or green coloration. This property is leveraged for priming andanticorrosive coating formulations for steel structures exposed to harsh environments. As a mordant, it helps bind other pigments like organic colors permanently to surfaces during the painting process, enhancing product performance and longevity. Leading paint and coating producers maintain iron (II) sulfate in their input raw material supply chains.
Pharmaceutical and construction uses
In the pharmaceutical industry, ferrous sulfate is prescribed as an oral supplementation for treating Iron deficiency conditions like anemia. It helps boost hemoglobin levels in the blood. Externally, it is present in some antifungal and antibacterial medications due to its disinfecting properties. The construction sector makes use of iron (II) sulfate for steel reinforced cement manufacturing. It protects reinforcing steel bars from corrosion when added to concrete mixtures. This preserves the strength and structural integrity of constructions over long service periods. Cement product quality testing also involves using iron (II) sulfate solutions to check setting behavior and soundness.
Global supply chain and pricing factors
The global supply chain network for iron (II) sulfate involves multiple stages from its production to end usage. Major producers export this chemical worldwide via seaborne shipping. China dominates the export market with over 60% share due to its large manufacturing base and competitive costs. However, increasing environmental regulations there are impacting supply. This has led importers to diversify sources to countries like India and European nations. Transportation and logistical costs remain key influencing price parameters for suppliers based on location. Iron (II) sulfate prices also fluctuate depending on demand cycles from key consuming industry segments. Any supply disruptions or increased production costs tend to harden prices in the international iron (II) sulfate industry over the short-term.
Latest consumption trends
Recent years have seen emerging consumption trends for ferrous sulfate. Its usage as a dietary Iron supplement in pharmaceutical preparations is growing notably, especially pediatric drops and tablets. This is driven by rising worldwide focus on anemia treatment. Water treatment plants upgrading to higher standards also contribute to steady long-term demand increase. However, developed nations have started regulating iron (II) sulfate loading concentrations due to environmental impact concerns. Alternative coagulants are being evaluated. Green cement technologies exploring substitutes for conventional Iron enrichment may marginally affect construction sector off-take in future. Overall, the inherent versatility of iron (II) sulfate guarantees continued importance as a major industrial chemical globally.
Get more insights on Ferrous Sulfate