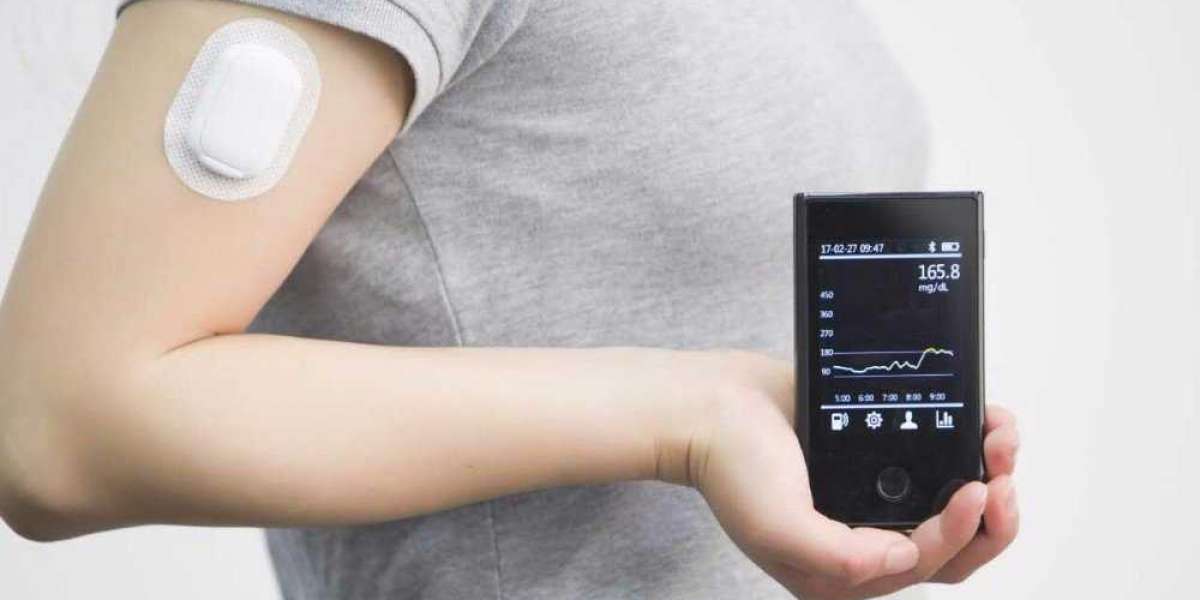
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices are medical devices used by patients with diabetes to constantly check glucose levels in the blood without the need for finger pricking. CGMs work by inserting a small flexible filament under the skin that measures interstitial fluid glucose levels every few minutes. The data is sent wirelessly to a receiver or smartphone and displays the user’s current glucose concentration as well as any trends indicating if levels are going up or down. Having constant real-time visibility into fluctuations helps people with diabetes better control their condition through proactive treatment.
Landscape in China
China has seen tremendous growth in its CGM in recent years driven by a large diabetic population and government support for new diabetes technologies. According to various reports, annual sales of CGM systems surpassed 35 million USD in 2020 compared to just 5 million USD in 2015. Domestic Chinese manufacturers have emerged as serious competitors to global leaders by developing their own China Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices platforms and negotiating bulk contracts with hospitals and insurance providers nationwide. Key players such as Ypsomed, Roche, and Medtronic currently account for over 60% of China’s CGM share but local upstarts are gaining ground rapidly.
Regulatory Approvals and Reimbursement
Obtaining regulatory approval and securing government reimbursement are essential for medical device firms looking to succeed in China’s CGM landscape. All CGM systems must first receive a Class III medical device license from the National Medical Products Administration before ing and sales. This involves rigorous clinical trials to prove safety and efficacy. Once approved, negotiations begin with the National Healthcare Security Administration to have the devices covered partially or fully by the national insurance scheme. Those that achieve wide coverage gain significant sales advantages over competitors with limited or no reimbursement access. More domestic CGM technologies have cleared these critical hurdles in recent years.
Leading Chinese Domestic Players
Several Chinese companies have released their own innovative CGM solutions to tap into rising demand.
- Deep Blue Technology: Based in Wuxi, Deep Blue produces the WatchOG glucose monitoring bracelet approved in 2019. It provides real-time readings through an app and goodAccuracy compared to international brands.
- TelCare: A Shanghai-based startup, TelCare received CFDA approval for its SmartGlucose CGM system in 2020 targeted at type 1 diabetes patients. The lightweight smart patch transmits to a companion app.
- Triage Technologies: Based in Beijing, Triage launched the MediSense Freedom CGM in partnership with Abbott. It features a small reusable transmitter granting wireless glucose readings to smartphones.
- QuanTech: Nanjing-based QuanTech released the QT-CGM professional CGM system in late 2020 for hospital and clinical use. The clip-on device transmits to a centralized monitoring hub.
These domestic players aim to provide more affordable, user-friendly CGM alternatives while meeting strict quality and safety standards. With support from government-backed programs, their shares will likely rise further over the next decade.
Get more insights on China Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices